Marketing Analytics
What it is, why you need it, and best practices. This guide provides definitions and practical advice to help you understand and establish world class marketing data analytics.
Marketing Analytics Guide
What Is Marketing Analytics?
Marketing analytics is the practice of analyzing marketing data from multiple systems to gain insights and make informed decisions. It helps you evaluate the effectiveness of your marketing efforts, track campaign performance, and understand customer behavior. By utilizing data-driven insights, you can optimize your marketing strategies and drive business growth.
Marketing Analytics Benefits
Marketing analytics is crucial because it allows you to make data-driven decisions and measure the effectiveness of your marketing efforts. By analyzing data and metrics, you can gain valuable insights into customer behavior, preferences, and market trends. This information helps you optimize your marketing strategies, target the right audience, allocate resources efficiently, and ultimately drive better business outcomes.
Key benefits of marketing data analytics include:
Demonstrate ROI
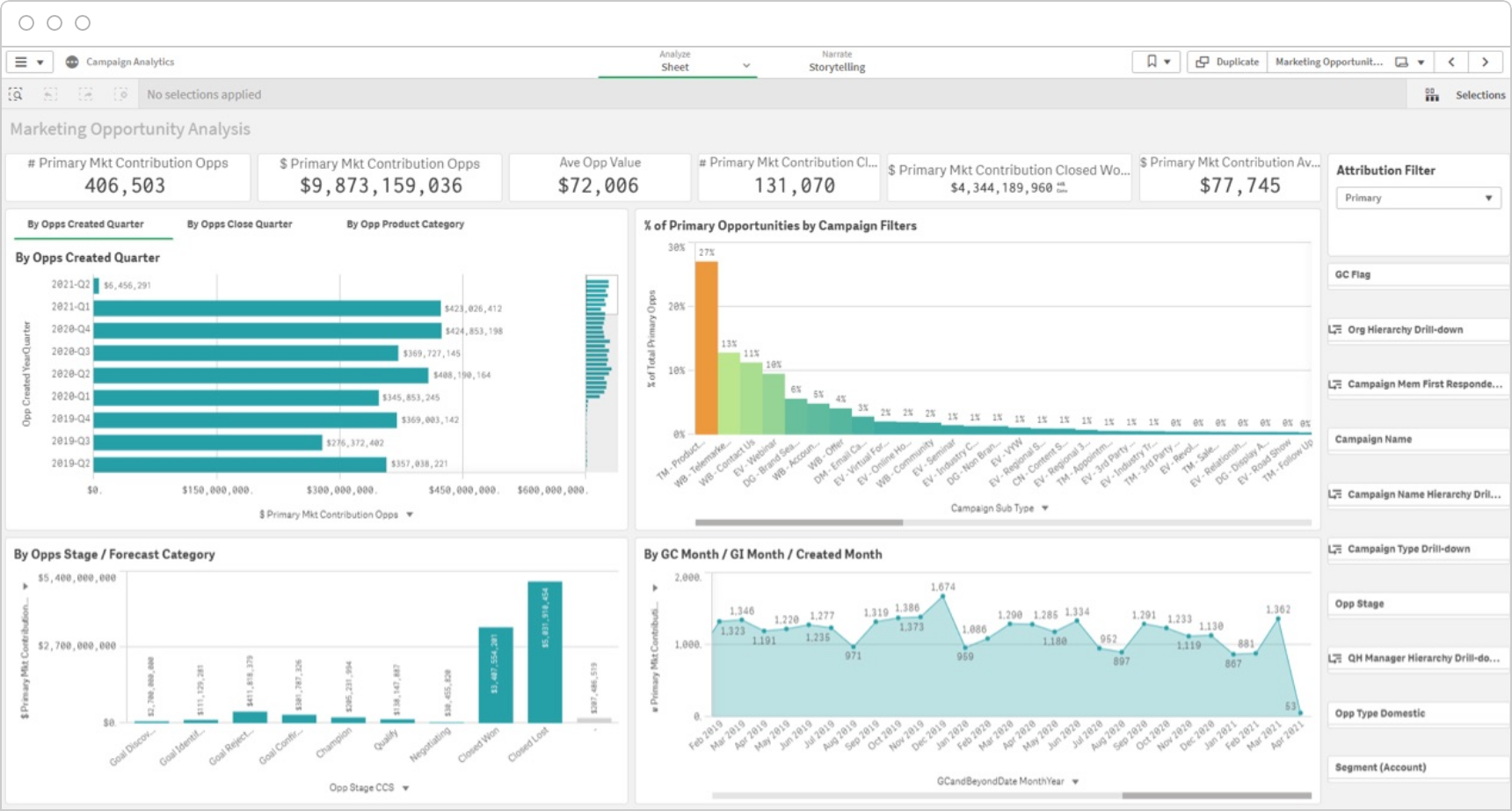
Track how your marketing efforts impact pipeline creation and revenue using accurate campaign attribution. Marketing analytics helps you break down data silos and analyze an integrated data set to measure across the entire funnel.
Optimize Investment & Mix
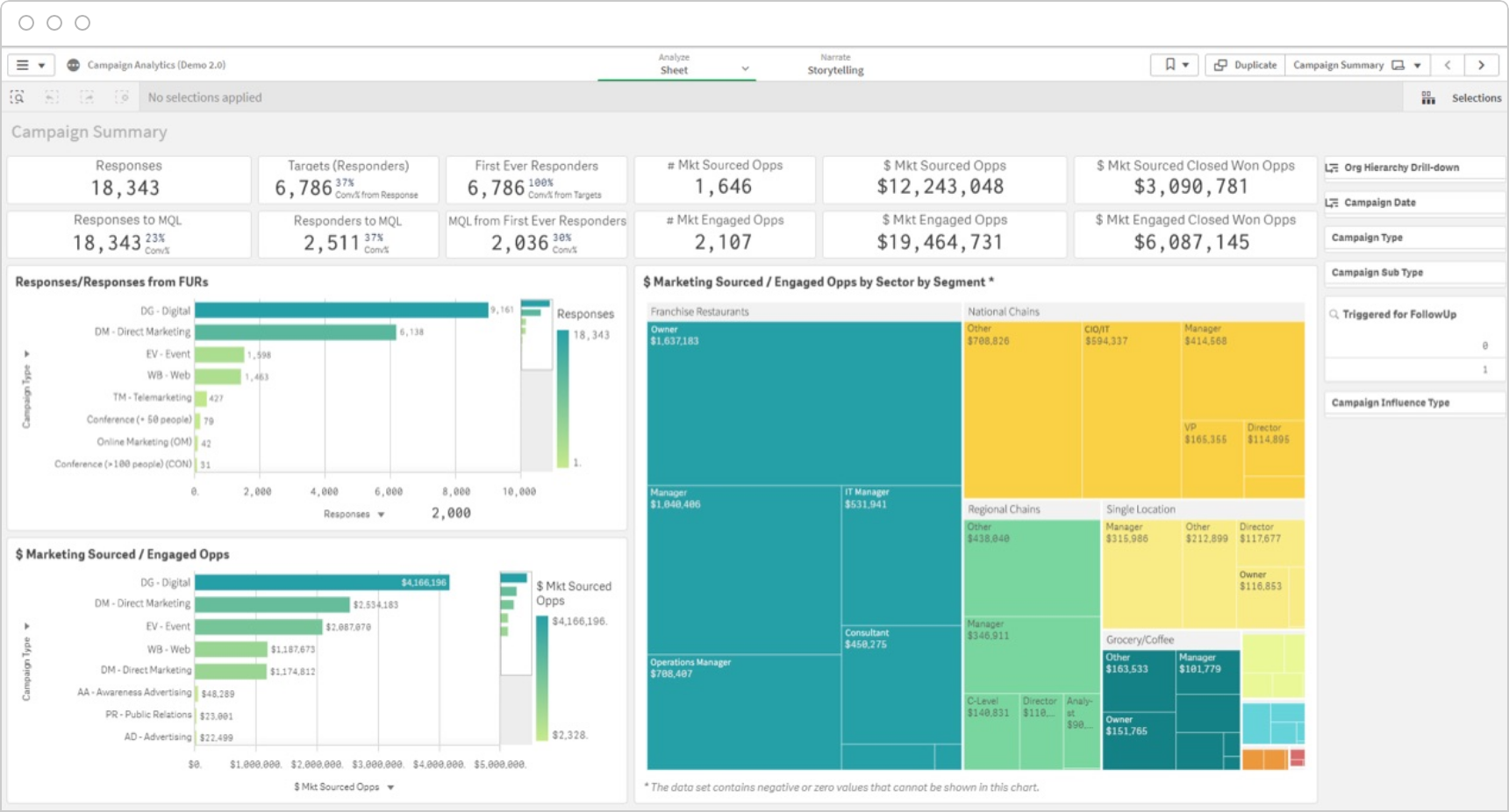
Marketing data analysis using multi-touch attribution lets you close the loop between campaigns and revenue to optimize budget and resource investments in channels.
Improve Campaign Planning and Scheduling
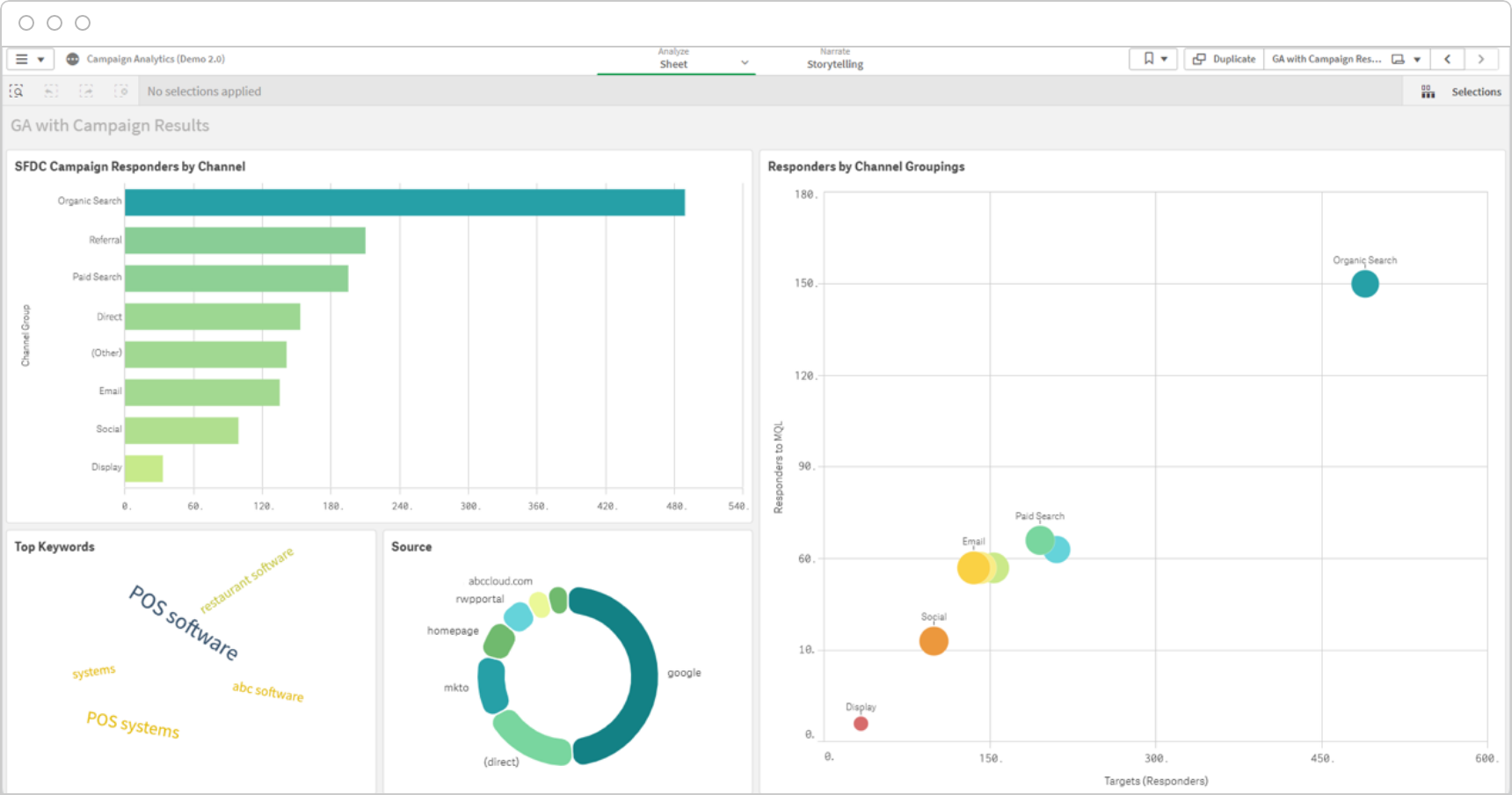
Strategically plan and schedule marketing campaigns, ensuring optimal timing, channel selection, and resource allocation to maximize effectiveness and reach.
Improve Campaign Performance
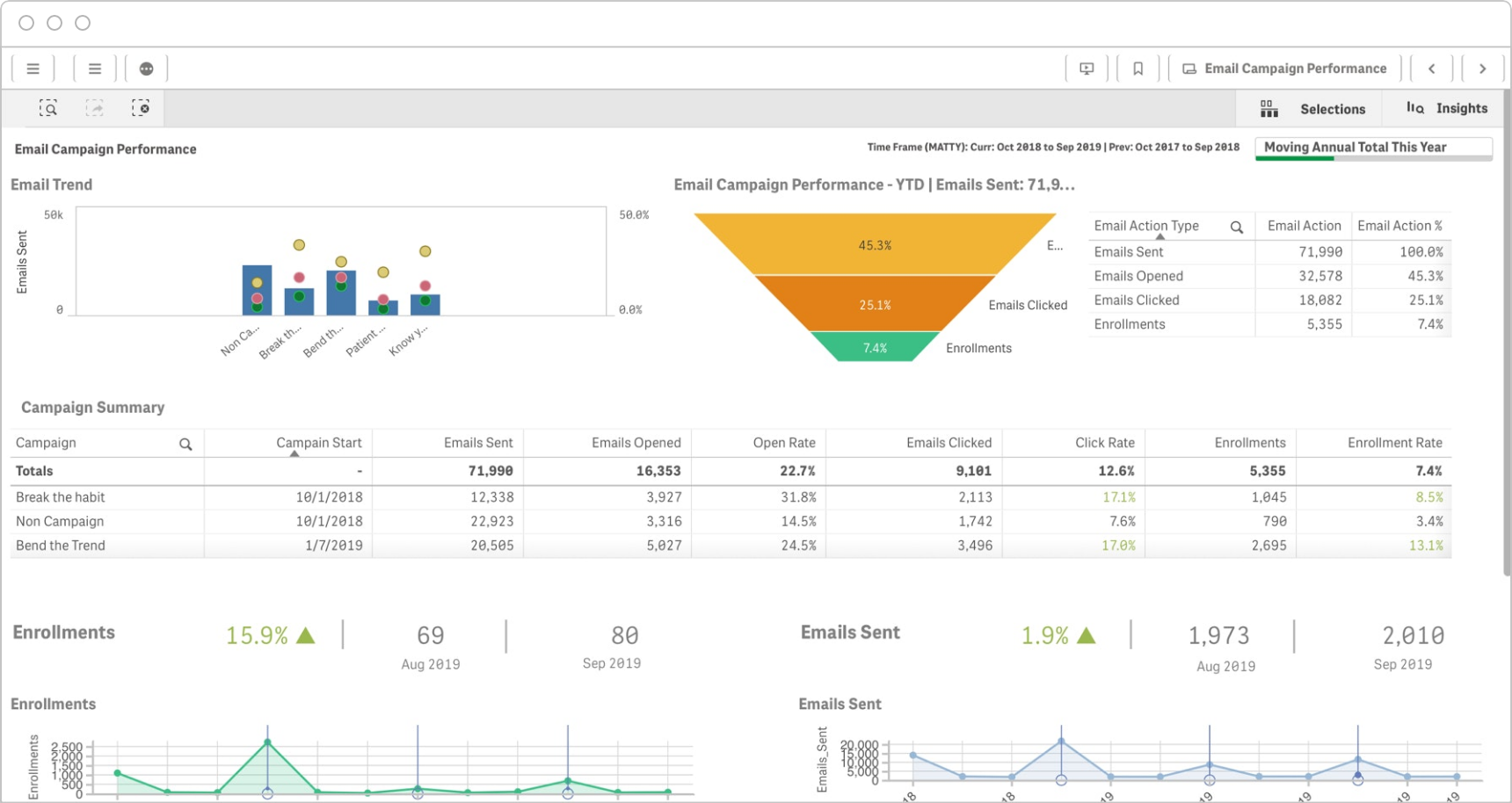
Increase conversion rates and revenue by knowing how tests of ad creative, messaging and pricing are impacting sales, not just front-end metrics like impressions or click-through rates.
Enhance Workflow Efficiency
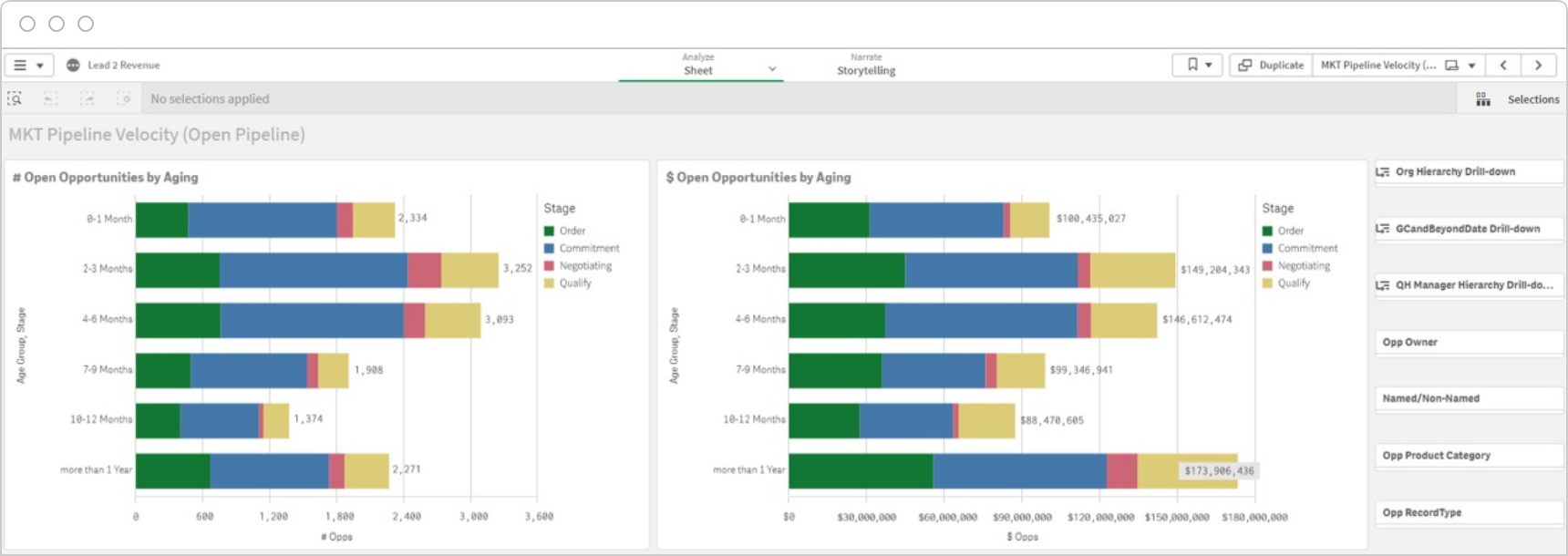
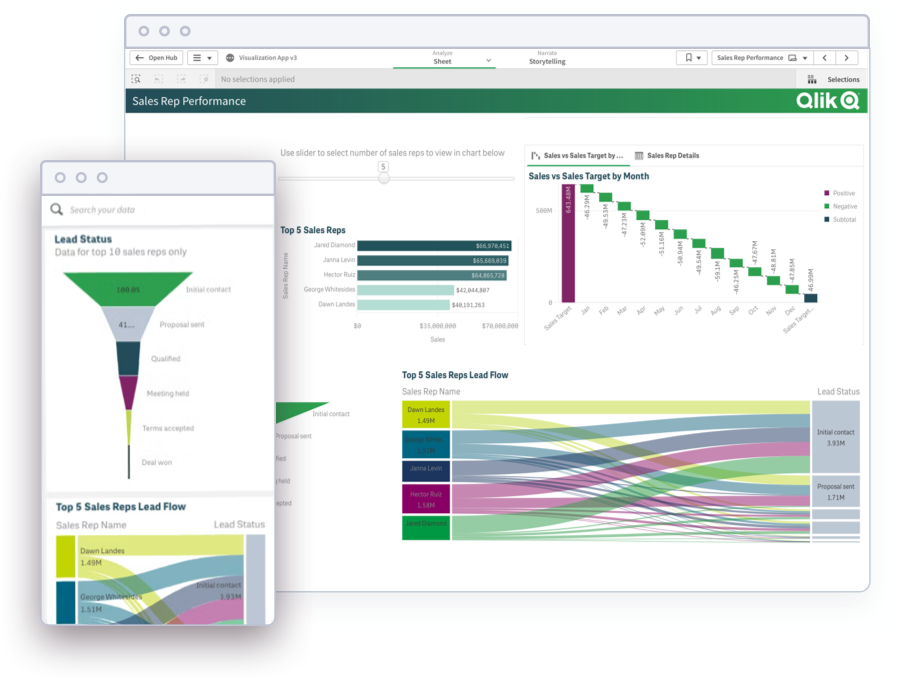
Optimizing marketing processes, systems, and workflows helps you identify bottlenecks, streamline operations, and enhance overall efficiency, resulting in improved productivity and resource utilization. This dashboard example identifies where prospects are getting stuck in your funnel.
Better Forecast and Track KPIs
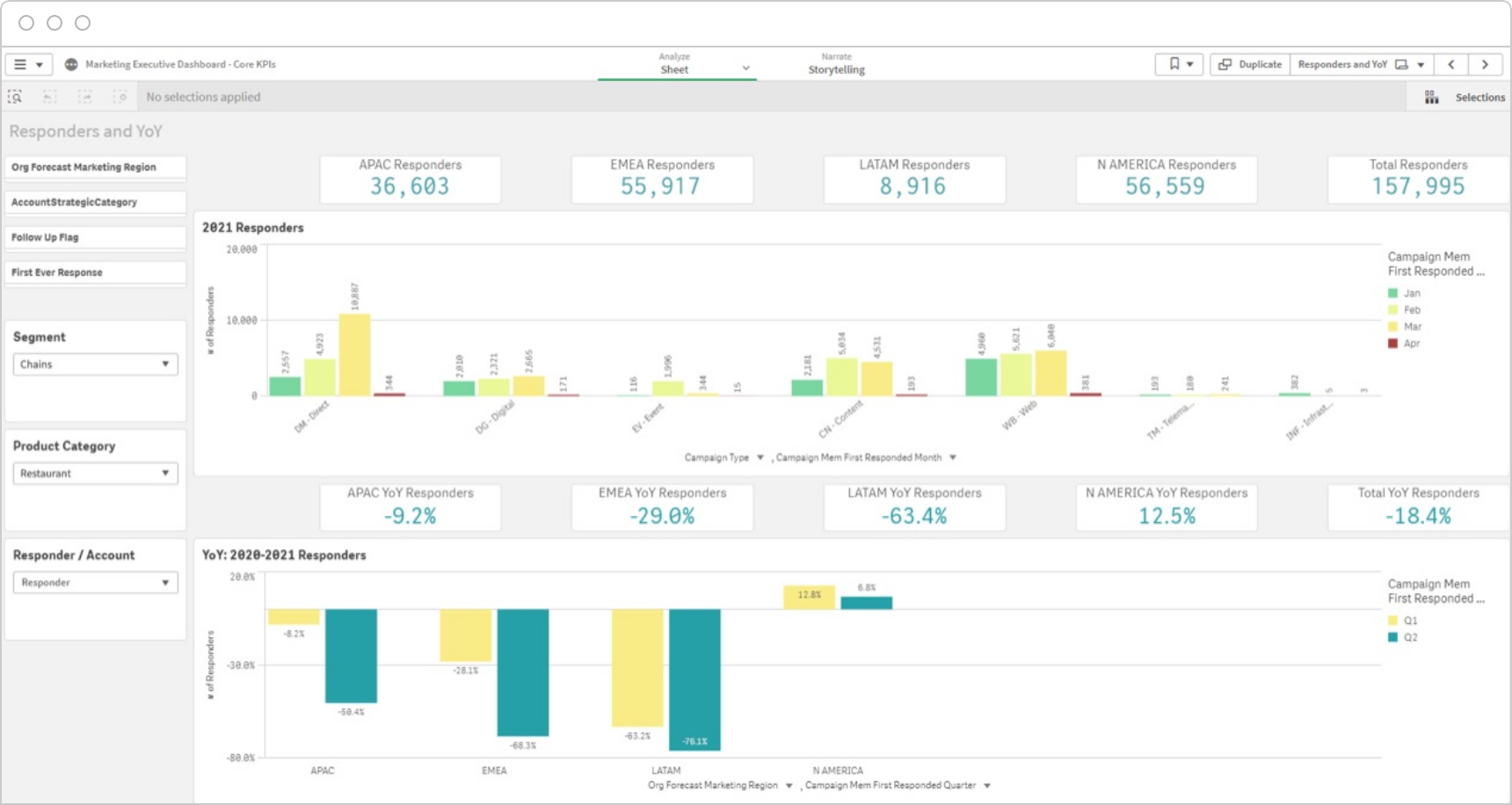
Forecast and track your performance to goals for KPIs. Having your dashboards refresh automatically reduces your reporting time and predictive marketing analytics uses statistical modeling, data mining techniques and machine learning to make accurate forecasts based on historical and current data.
Other benefits of marketing data analysis include:
- Customer segmentation involves dividing your company's customer base into distinct groups based on shared characteristics and behaviors to better target marketing efforts and tailor messages to specific segments.
- Competitor analysis involves assessing and analyzing the strategies, tactics, strengths, and weaknesses of competitors in the market to gain insights and identify opportunities for differentiation and competitive advantage.
- UX (User Experience) performance analytics focuses on evaluating and measuring the usability, effectiveness, and satisfaction of users when interacting with a company's digital assets or platforms, providing insights to improve user experiences and drive better engagement.
- Customer lifetime value (CLV) analytics quantifies the total value a customer brings to your business over their entire relationship, helping you understand the long-term profitability of customers and enabling you to make informed decisions on customer acquisition, retention, and personalized marketing strategies.
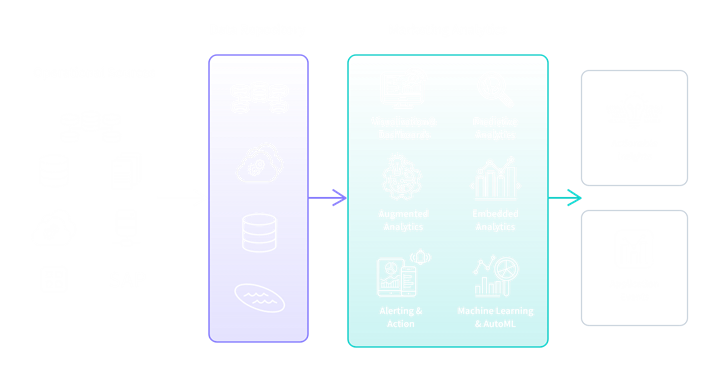
How Marketing Analytics Works
Modern marketing data analytics is powered by a cloud-based, end-to-end data integration and analytics platform. This platform helps you manage data across its lifecycle as well as perform the necessary types of analytics.
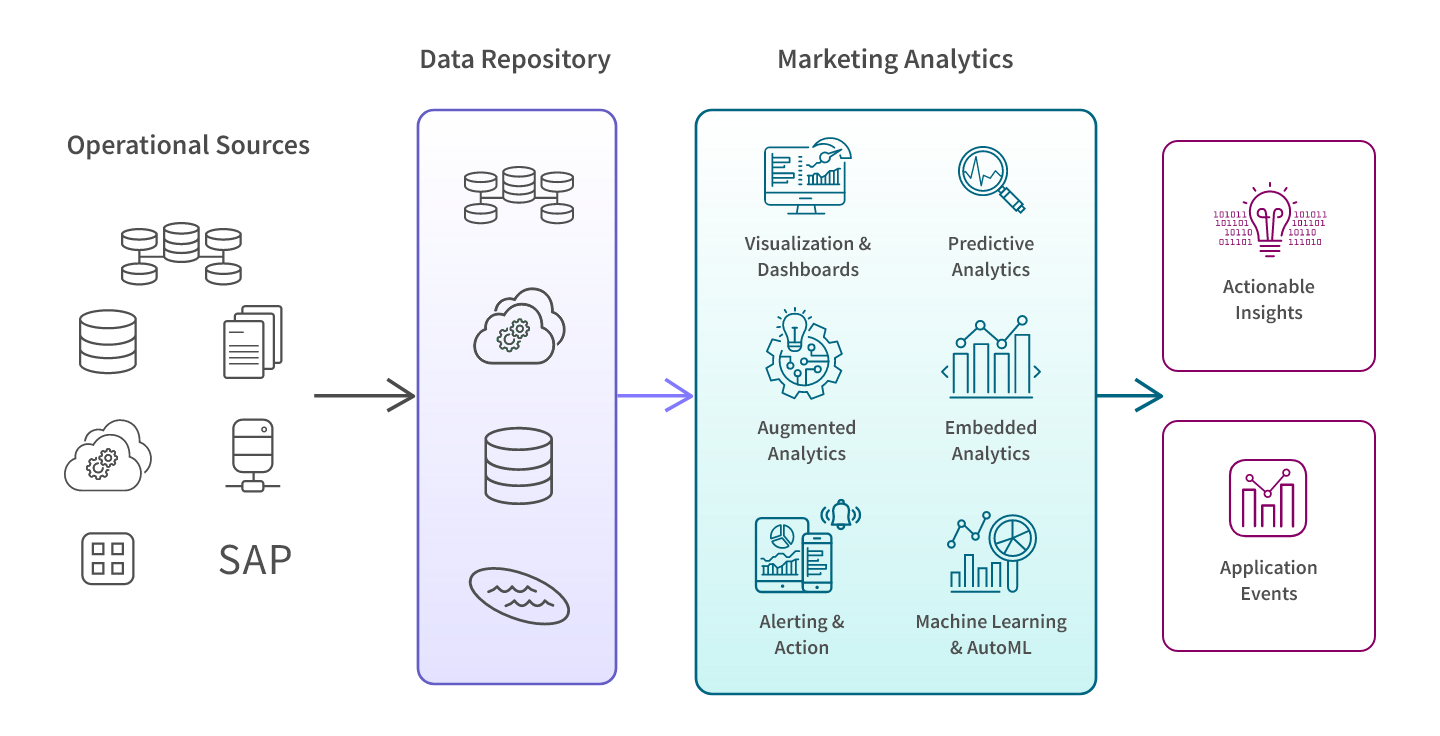
Let’s walk through the diagram above.
- Data is sourced from your marketing operational systems such as ad platforms, CRM, marketing automation, web analytics, and IoT/product. Data from third-parties such as partners, data brokers, and merchants can also be included.
- This data is extracted, transformed, and combined into a repository such as a data warehouse or data lake, typically in the cloud. This gives you a comprehensive view across the full customer lifecycle.
- Your marketing analytics tool makes it easy for you to use this data to perform different types of analysis. For example, you could use predictive marketing analytics to project new customers for a campaign.
- Marketing analytics software also allows you to create interactive visualizations and dashboards which help you identify patterns and develop insights into KPIs such as customer lifetime value, acquisition cost, and conversion rates. Some tools allow you to embed your analytics into other applications, allowing users to gain insights within their regular workflows.
- Top tools go further and enable you to leverage AI analytics capabilities such as automated machine learning (AutoML), predictive analytics, and prescriptive analytics. Augmented analytics guides you by automatically surfacing insights and relationships in your data and providing recommendations of angles for you to explore.
- This results in insights which you can action on and/or trigger alerts and actions in other systems.
Explore these top data analytics resources
-
BARC’s BI & Analytics Survey 23: Qlik Highlights
BARC, a leading enterprise software analyst firm, talked to real BI users to analyze and compare leading BI and Analytics products. Users ranked Qlik Sense® #1 in Performance Satisfaction, Dashboards, and Project Length in its peer groups. -
Know the trends
Learn about the top 10 BI and data trends and how advanced analytics can help you navigate today’s fast-paced world.
Marketing Analytics Types
Here are the four types of data analytics in marketing and the questions answered by each:
| Type | Question Answered | Example |
|---|---|---|
|
What happened?
|
How many leads did we acquire last quarter?
|
|
|
Why did it happen?
|
What’s causing our drop in site traffic?
|
|
|
What will happen?
|
What will be the customer response to our upcoming product launch?
|
|
|
What should we do?
|
What specific actions should we take to maximize conversion rates?
|
Modern Analytics Demo Videos
See how to explore information and quickly gain insights.
- Combine data from all your sources
- Dig into KPI visualizations and dashboards
- Get AI-generated insights
Marketing Attribution Models
Marketing attribution models are used to understand and evaluate the impact of marketing channels and activities on customer conversions or sales. Different models offer varying perspectives and insights. You should choose the model that aligns best with your objectives and understanding of customer behavior.
Media Mix Models (MMM) are marketing attribution models that analyze historical data to determine the contribution and impact of various marketing channels on overall sales or conversions. They use statistical techniques to evaluate the effectiveness and ROI of different media channels and marketing activities, considering factors such as ad spend, reach, frequency, and market conditions.
Multi-Touch Attribution (MTA) models attribute credit for conversions or sales to multiple touchpoints along the customer journey. These models assign value to each interaction or touchpoint a customer has with marketing channels and activities, providing insights into the specific channels, campaigns, or tactics that influenced a conversion. MTA methods can vary, including rule-based models, time decay models, and algorithmic approaches.
First-Touch Attribution assigns all credit for a conversion or sale to the first interaction or touchpoint a customer had with a marketing channel. It emphasizes the initial touchpoint's role in capturing the customer's attention and initiating their journey.
Last-Touch Attribution attributes all credit for a conversion or sale to the last interaction or touchpoint a customer had before completing the desired action. It focuses on the final touchpoint's role in driving the customer to convert or make a purchase.
Linear Attribution distributes equal credit across all touchpoints a customer had during their journey. It assumes that each touchpoint contributes equally to the conversion or sale, regardless of its position in the customer journey.
Time Decay Attribution gives more credit to touchpoints that occur closer to the conversion or sale. It assumes that touchpoints closer in time to the conversion had a more significant influence on the customer's decision. Marketing attribution models are used to understand and evaluate the impact of marketing channels and activities on customer conversions or sales. Different models offer varying perspectives and insights. You should choose the model that aligns best with your objectives and understanding of customer behavior.
U-Shaped (Position-Based) Attribution assigns a higher percentage of credit to the first and last touchpoints, with the remaining credit distributed evenly among the touchpoints in between. It acknowledges the importance of both initial and final interactions in shaping the customer's journey.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are examples of marketing analytics?
Examples of data analytics in marketing include analyzing website traffic and engagement metrics, conducting customer segmentation and profiling based on demographics and behaviors, measuring the return on investment (ROI) of marketing campaigns, tracking social media performance and sentiment analysis, and using predictive modeling to forecast future customer behavior and preferences.
What degree do you need for marketing analytics?
To pursue a career in marketing analytics, a bachelor's degree in fields such as marketing, business analytics, data science, statistics, or a related discipline is typically required. However, some positions may prefer or require a master's degree or higher level of education, particularly for advanced roles or in-depth data analysis. Additionally, gaining practical experience through internships, certifications, or specialized training in analytics tools and techniques can further enhance your job prospects in the field of marketing data analytics.
How is marketing analytics as a career?
Marketing analytics offers you a promising and rewarding career path. With the increasing availability of data and the growing importance of data-driven decision-making in marketing, there’s a high demand for professionals skilled in marketing data analytics. This career allows you to work at the intersection of marketing and data, leveraging analytical skills to extract insights, optimize marketing strategies, and drive business growth. You have the opportunity to work in diverse industries, collaborate with cross-functional teams, and contribute to key business decisions. It’s a dynamic field that offers continuous learning and growth opportunities as technology and analytical techniques evolve.
